Thunderbolt 4 Explained: Everything You Need to Know

With the development of high speed data transmission and multifunctional connection Thunderbolt technology has become one of the trendiest standards in the world. The emergence of Thunderbolt 3 and Thunderbolt 4 has transformed the interaction and connection between us and our devices. However, How do they differ and what could offer you an improved digital experience?
This detailed guide takes you on a journey through thunderbolt 3 vs 4 discussion on their capabilities, advantages, and features. Whether you’re a technician, a buyer, or just someone looking for fast, secure data transfer, it’s crucial to understand the differences between the different versions of Thunderbolt technology and their relationship to the USB C connector when making your choice.
What is Thunderbolt?
Thunderbolt was created as an Intel cooperative venture along with Apple which provides rapid transmission of data and connectivity capabilities. It is an all-in-one interface that brings together data transfer, video output, and power delivery for devices.
The first technology of this kind originally appeared in 2011 under the name of Thunderbolt. It was designed with an aim to overcome shortcomings introduced by earlier connection standards. The device makes use of both PCI Express PCIe and DisplayPort technologies, allowing for quick data exchange and quality high resolution image transmission.
In earlier generations of Thunderbolt, such as Thunderbolt 1 and Thunderbolt 2, a Mini DisplayPort connector was used. However, with the introduction of Thunderbolt 3 and Thunderbolt 4, a more versatile and capable connector, namely the USB-C connector, is employed. The USB-C connector offers a range of benefits, including higher data transfer speeds, support for multiple protocols, and the ability to deliver power to connected devices.
Key Features of Thunderbolt:
- High Data Transfer Speeds: With this said, Thunderbolt technology is exceptionally swift in transmitting massive data as it facilitates real-time transfer of huge documents or data-intensive work. For instance, Thunderbolt offers 40 Gigabits per second (Gbps) and 20 Gbps.
- Video and Display Capabilities: A single Thunderbolt 4 port currently supports one 120Hz 4K display + two 60Hz 4K display. Or a single Thunderbolt 4 port can support multiple high-resolution displays simultaneously, including 4K displays with varying refresh rates. There is speculation that future Thunderbolt versions, like Thunderbolt 5, may support an increased number of high-resolution displays.
- Power Delivery: USB connectors with thunderbolt technology are able to provide power; this means that you can get data and power transfer in one single cable. It does away with the need for extra power adapters as it is self-powered.
- Device Compatibility: The Thunderbolt protocol supports connectivity for numerous devices, including computer systems, portable computers or laptops, external storage units such as hard disk or external drive, screens, audio interfaces. The product is an all-in-one cable that connects various electronic devices, resulting in one less array of wires and ports.
- Daisy-Chaining: Being daisy chained ready, the Thunderbolt also enables connection of various devices through one port. It supports easy configuration and effective utilization of ports available.
Thunderbolt Technology Communication Mode.
When purchasing USB-C cables, it’s crucial to consider their capabilities. While both Thunderbolt and USB ports are compatible with USB Type-C cables, it’s important to note that only Thunderbolt-specific cables should be used for Thunderbolt connections. Thunderbolt combines PCI Express (PCIe) and DisplayPort (DP) into two serial signals, and additionally provides DC power, all in one cable. Up to six peripherals may be supported by one connector through various topologies. Thunderbolt cables are versatile and can also serve as full-featured USB cables, making them a universal option that works with any USB-C port.
Because a Thunderbolt cable uses a USB C connector type, it has four shielded SuperSpeed pairs (often called “channels”), each capable of transmitting data at 20 Gb/s. (Get an in-depth look at USB C pin array capabilities.)
Thunderbolt ports are equipped to dynamically detect the capabilities of connected cables and devices. They can activate one or multiple of the following connection modes:
- USB Only Mode: This mode is triggered when connecting devices or cables that lack Thunderbolt support. In this case, the Thunderbolt port activates the USB controller to support USB 3.x or 2.0 signaling. Click for more detailed USB standards information.
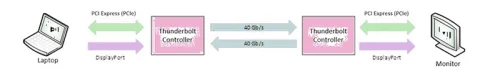
- Thunderbolt Alt Mode: Alt Mode is a functional extension of USB-C which enables the USB connection to carry non-USB signals. Alt Mode(s) are optional capabilities that are unique to the USB-C connector or port that allow technologies, like DisplayPort and Thunderbolt 3, to be transmitted. By pairing a Thunderbolt cable and device, the Thunderbolt controller combines two lanes in each direction to establish two full-duplex, bidirectional channels with a speed of 40 Gb/s each.
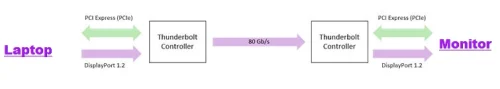
- DisplayPort Alt Mode: When connecting a DisplayPort monitor or adapter, the Thunderbolt controller engages the DisplayPort Alt Mode, remapping all four USB-C lanes to function in a single direction. This creates a substantial 80 Gb/s link, making it suitable for driving an 8K HDR2 display.
- PCIe Mode: Using the PCIe standard Thunderbolt may transmit data by means of the PCIe mode. Peripheral Component Interconnect Express or PCIe is an ultra-high speed serial bus interface commonly used to connect peripherals like graphics cards, network adapters, storage devices, and other expansion cards onto the motherboard of a PC.
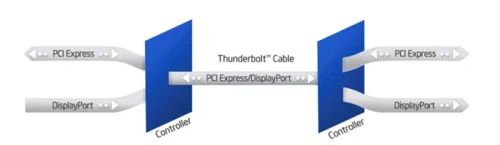
- USB/DP Combo Mode: This mode combines both USB and DisplayPort functionalities. The Thunderbolt port allocates the four USB-C lanes for use in both DisplayPort and USB operations.
- Thunderbolt Networking Mode: Designed for facilitating direct Ethernet connections between two or more Thunderbolt-enabled computers. This mode enables resource sharing, file copying, transferring, or printing across connected devices.
- Power Delivery and Charging: Thunderbolt technology encompasses power and charging support for host devices and connected peripherals through USB Power Delivery (USB-PD). This includes the allocation of 15W for bus-powered peripherals.
These distinct Thunderbolt communication modes play a pivotal role in ensuring compatibility and optimizing performance across various applications and devices. Understanding their functionalities is paramount for harnessing the full potential of Thunderbolt technology.
What is Thunderbolt 4?
Thunderbolt 4, the latest version of Thunderbolt technology, builds upon the foundation established by its predecessors. Developed by Intel over a decade ago, Thunderbolt technology has continuously evolved to enhance device connectivity and capabilities. Thunderbolt 4 utilizes the USB-C connector type, leveraging its versatility and widespread adoption. With Thunderbolt 4, users can benefit from a range of important features that further enhance connectivity and device capabilities.
These ports (high-speed Thunderbolt 4 technology) harness the power of the CPU to improve data and video performance. Thunderbolt 4 is a new standard that enables lightning-fast data transfer, enabling smooth, interruption-free transfer of large files, high-resolution videos, and more data-intensive activities.

Advantages:
Connecting peripherals or I/O to a PC using Thunderbolt 4 is much more advantageous than any other type of port. Here are some key benefits of Thunderbolt 4:
- Flexibility: Versatility comes with Thunderbolt 4 ports. However, unlike other ports meant for particular duties, Thunderbolt four is designed to handle several jobs concurrently. This one port USB docking station gives it the capability of carrying out ultra-high speed data transfer, providing a video signal to an external monitor; as well as giving power to other suitable equipment. It facilitates unrestricted interconnects and enables optimal utilization of ports.
- Bandwidth: Bandwidths offered by thunderbolt 4 ports are significant. Thunderbolt 4’s bidirectional bandwidth is 40 Gbps, allowing for rapid data transfer. That is, it enables quick and efficient movement of data to and from external storage devices. Furthermore, with only one Thunderbolt 4 port, four USB peripherals can be connected and up to five Thunderbolt devices are supported, making it more flexible in terms of device arrangement.
- Versatile Connectivity: The Thunderbolt is made to work with multiple connection protocols. These ports are all backward-compatible, meaning they will work with older Thunderbolt, USB, DisplayPort, and PCIe ports. The compatibility allows Thunderbolt 4 ports to work with many kinds of devices, extending the range of possibilities available to users and increasing the chances of interoperability. In addition, the Thunderbolt 4 ports utilize standard USB-C type connectors, which facilitate convenience and compatibility with multiple devices.
- Daisy Chain Functionality:One of Thunderbolt’s defining features is its daisy chain functionality, a concept that empowers a single peripheral port to accommodate multiple devices. To execute this seamlessly, Thunderbolt peripherals must feature both inbound and outbound connector ports. The chain begins with the first device connected to the computer, and each subsequent device links to the previous one’s outbound port. While this offers remarkable flexibility, overloading the chain with too many devices can lead to bandwidth saturation, affecting overall performance.
For high-performance users requiring versatile connectivity, Thunderbolt 4 is the right way to go. By having all your transport needs catered for with one single cable, be it for bulk data transfer, power to external devices or connecting multi peripheral products, Thunderbolt 4 is a total solution that marries speed, adaptability and versatility.
Applications:
Thunderbolt 4 is a strong and adaptable connectivity solution. It can do a lot. Here are some examples:
- Thunderbolt Devices: Thunderbolt 4 allows you to connect many devices with the Thunderbolt logo on them. This includes docks, displays, storage devices, and video capture devices. Docks and cables with Thunderbolt 3 are completely compatible with ports that have Thunderbolt 4. To use older Thunderbolt devices you’ll need an adapter.
- External Monitors: Connecting multiple screens to your computer becomes possible when using Thunderbolt 4. Using a single port, you can connect two 4K 60Hz DisplayPort or HDMI monitors if you’re using an adapter or compatible dock. Monitors designed for thunderbolts can be connected directly for an even better display experience.
- Storage Expansion: With Thunderbolt 4 you can add high-speed external SSDs (Solid-State Drives) to your system to increase storage capacity, this allows data transfer speeds that rival internal drives which is ideal for tasks needing fast and reliable storage solutions.
- USB Peripherals: With Thunderbolt 4 enabled, you can connect a range of USB peripherals. This includes mice, keyboards, controllers, and headsets. You can cater them to different user needs such as gaming and productivity tasks.
- PCIe Devices: If you have PCIe devices laying around, Thunderbolt 4 has your back. You’re able to access these devices with the use of an expansion chassis that supports PCIe products. For example, you can get video capture devices used in live-streaming gameplay. Or any other specialized hardware that requires PCIe connections.
- Networking: In case you need to connect your computer to a high-speed network, Thunderbolt 4 offers networking capabilities. It has support for high-speed 10 Gigabit Ethernet networks via an adapter. On top of that, it allows you to create a peer-to-peer network between two computers using cables. This way you can send large data files from one PC to another which is useful when upgrading systems.
- Charging: Lastly, Thunderbolt 4 works as a quick charger for various devices. Using its ports to quickly charge your phone or even lightweight notebook PCs that require less than 100W of power is possible. Additionally, it’s also compatible with other USB devices for efficient charging.
The Development History of Thunderbolt.
Intel introduced Thunderbolt in 2009 under the code name Light Peak. making its debut exclusively on Mac computers before extending its reach to PCs. Unlike USB devices, Thunderbolt peripherals must undergo rigorous certification by Intel, ensuring top-notch quality and performance.
As it evolved through various versions of thunderbolt, it underwent significant advancements, each contributing to enhanced data transfer speeds and cross-compatibility. The Apple Connection: Apple played a pivotal role in popularizing Thunderbolt, primarily driven by the aim of reducing cable clutter in its ultraportable laptops like the MacBook.
The Early Stages of Thunderbolt Development.
During its nascent stages, Thunderbolt was originally conceived as Light Peak, an optical interface standard. However, the idea of using optical technology was eventually shelved in favor of conventional electrical cabling. This transition simplified implementation, employing the existing DisplayPort technology with its mini-connector design. DisplayPort was a strategic choice among video interfaces due to its unique feature of an auxiliary data channel, setting it apart from HDMI and DVI. Learn more about the differences between Thunderbolt, DisplayPort, and HDMI.
To establish the data link component of Thunderbolt, Intel wisely adopted the well-established PCI-Express specification. This choice was logical since PCI-Express had a proven track record as a connector interface for internal components within processors.
Just like any other technology, when they came out with the second version they doubled the bandwidthto 20Gbps. They also included support for Displayport 1.2 which allowed signals to be driven to 4Kisplays.
The Era of Thunderbolt 3
In 2015, Thunderbolt technology took a significant step forward with the introduction of Thunderbolt 3. This iteration introduced innovative changes, breaking free from DisplayPort technology and transitioning to USB 3.1 with a new Type-C connector. This transition opened up new possibilities, including the simultaneous transfer of power and data signals.This shift in physical connectivity also brought the addedbenefit of up to 100 watts of power deliveryhrough USB Power Delivery (USB PD). This meant that Thunderbolt 3 ports could not only transfer dataand video signals but also serve as a power source for charging devices. including laptops andsmartphones.
With Thunderbolt 3, it became conceivable for a laptop with a Thunderbolt 3 port to receive power via the cable while simultaneously sending video and data to a monitor or base station. Thunderbolt 3 offered exceptional transfer speeds, reaching up to 40 Gbps, more than sufficient to support multiple devices seamlessly.
The Advancements of Thunderbolt 4
Thunderbolt 4, announced in early 2020, made its way to the market later in the same year, promising improvements without a significant speed boost. Although the data transfer rates remained the same, but Thunderbolt™ 4 technology advances the universal connectivity standard by doubling the minimum video and data requirements of Thunderbolt™ 3 technology and by expanding end-to-end solution capabilities. For instance, it could now support two 4K displays or a single 8K display, making it a powerful choice for high-resolution multimedia needs. Cables extended their reach to two meters, allowing for more flexibility in device placement.
Moreover, Thunderbolt 4 set specific minimum standards for peripheral devices. These standards included support for wake-from-sleep functionality for docks, defined power ratings for laptop charging, and enhanced security measures to protect against potential threats, such as Thunderspy attacks.
One of the most significant developments in Thunderbolt 4 is its full compatibility with the USB4 protocol and data rates. While this cross-compatibility has introduced notable advantages, it has also generated some visual confusion, as ports for Thunderbolt 4, Thunderbolt 3, and USB4 now share a similar appearance.
| Standard | Connector | Video | Data Rate | Power | Max Cable Length |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thunderbolt 1 | Mini DisplayPort | 2560 x 1600 (single display) | 2 x 10 Gbit/s | 10W | 3M |
| Thunderbolt 2 | Mini DisplayPort | 4K (single display), 2560 x 1444 (dual display) | 20 Gbit/s | 10W | 3M |
| Thunderbolt 3 | USB-C | 4K @ 120 Hz (single display), 5K @ 60 Hz (single display), 4K @ 60 Hz (dual display) | 40 Gbit/s | 100W | 0.5m (passive) 2m (active) |
| Thunderbolt 4 | USB-C | 8K @ 60 Hz (single display), 4K @ 60 Hz (dual display) | 40 Gbit/s | 100W | 2M |
The progression of Thunderbolt from its inception to Thunderbolt 4 showcases its evolution as a powerful and versatile connectivity solution, enabling high-speed data transfer, video output, power delivery, networking, and expansion options. Its widespread adoption has revolutionized the way we connect and interact with our devices, opening up new possibilities for productivity, creativity, and entertainment.
What is The Difference Between Thunderbolt 3 and Thunderbolt 4?
A maximum throughput of 40Gbps, charging range from 15 watts to 100 watts, and offering support for 10Gbps networking are just some of the similarities between Thunderbolt 4 and Thunderbolt 3. Despite this, there are notable advancements that set Thunderbolt 4 apart upon examination. Although not immediately noticeable, this newer technology excels in ways the 3rd edition cannot. The USB Type-C connector remains intact, however, with Thunderbolt 4, you can expect significant improvements in its performance.
Beneath the exterior, Thunderbolt 4 has numerous exceptional features. It raises the minimal necessities for both video and data in contrast to Thunderbolt 3. Thunderbolt 4 is remarkable in its Thunderbolt 4 supports 4K to dual monitors or 8K to a single monitor, while Thunderbolt 3 supports 4K to dual monitors or 5K to a single monitor. As an added advantage, whereas Thunderbolt 3 configurations are compelled to process a 16Gbps data rate through PCI Express, Thunderbolt 4 doubles the requirement to a substantial 32Gbps. For those who often need to transfer sizable files like high-quality videos and other sizable data sets to their computer for editing purposes, the added bandwidth is of great value.
Equipped with four ports, Thunderbolt 4 leads to superior peripherals, such as docks and monitors. With only two ports on Thunderbolt 3 devices, this is a significant upgrade. It’s worth noting that contemporary lightweight laptops can be charged using USB Type-C through at least one of their Thunderbolt 4 ports, requiring no more than 100 watts. Best thunderbolt 4 dock connections with laptops necessitate support for wake-from-sleep operation when connected to keyboards or mice. Not only that, but Thunderbolt 4 cables are also explicitly designed to sustain 40 Gbps throughput for as long as two meters – a considerable advancement from the existing passive Thunderbolt 3 cable that can go as far as half a meter.
Thunderbolt 4 hubs offer improved charging and wake-from-sleep capabilities, allowing for easier organization in your workspace. With the ability to connect six peripherals in daisy-chain fashion, multiple devices no longer require a direct link to your computer. Longer cables also contribute to a less cluttered and more flexible setup, making office life a breeze.
| Thunderbolt 3 VS Thunderbolt 4 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Features | Thunderbolt 4 | Thunderbolt 3 | |
| Data Transfer | 40 Gbps | 40 Gbps | |
| Video | Two 4K Monitors; One 8K Monitor | Two 4K Monitors; One 5K Monitor | |
| Power/Charging | Up to 100W | Up to 100W | |
| Daisy-Chaining | Yes (up to 6 devices) | Yes (up to 6 devices) | |
| Cable Length | 2m | 0.5m | |
| Connector | USB-C | USB-C | |
Are Thunderbolt 4 and USB C the Same?

Thunderbolt and USB-C cables and ports are not the same, although they share a physical connector. Thunderbolt 4 is a high-speed data transfer and peripheral connection technology developed by Intel. It offers significantly faster data transfer speeds, more advanced capabilities, and greater versatility compared to USB-C.
Thunderbolt 4 is designed to deliver a maximum throughput of 40Gbps, support multiple 4K or 8K displays, and provide up to 100 watts of power delivery. It also allows daisy-chaining multiple devices and has stricter certification standards.
USB-C, on the other hand, refers to the physical connector type, not a specific data transfer or charging technology. USB-C can support various data transfer speeds and power delivery levels, depending on the USB specification it adheres to (such as USB 2.0, USB 3.1, usb 3.2, or USB 4). While USB-C is versatile and widely adopted, it typically offers lower data transfer speeds and power delivery capabilities compared to Thunderbolt 4.
So, we can say that Thunderbolt 4 is a specific high-speed data transfer and peripheral connection technology that uses the USB-C connector but offers superior performance and features compared to the more general USB-C standard.
USB 4 VS Thunderbolt 4.
Thunderbolt 4 is based on the same underlying protocol as USB4—the two are tightly connected, with all Thunderbolt 4 devices supporting USB4, but fundamentally different in several ways. They both use a single USB-C connector such as a Thunderbolt 3. In essence, USB4 has more added features than Thunderbolt 4.
Built on USB4 protocols, all Thunderbolt 4 devices are USB4 compliant. Nevertheless, USB4 is a separate category distinctive from fully validated Thunderbolt 4 devices that do not offer similar powers and abilities.
Like Apple’s version of Thunderbolt 3, Thunderbolt 4 always delivers a full 40 Gbps bandwidth. In contrast, USB4 initiates from a rate of 20Gbps and may scale up to match the 40Gbps rate of thermbolt 4 under specific conditions. Click to learn more detailed USB4 protocol information.
- When it comes to display connectivity, USB4 allows for one display, while Thunderbolt 4 supports two 4K displays.
- On the other hand, USB4 enables hub and dock manufacturers to create powerful hubs and docks with less certification costs since they will not need to apply for the expensive Thunderbolt certification. Nonetheless, such a situation would lead to an impartially different level of quality in the USB4 market comparable to that of USB-C hubs today.
- On one hand, such products as Thunderbolt are always checked, so they comply with higher quality demands. Thus, it is foreseen that the Thunderbolt 4 devices would provide a standard high degree of quality and performance.
| USB4 vs Thunderbolt 4 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Features | USB4 | Thunderbolt 4 | |
| Maximum Throughput | Starts at 20Gbps, can reach 40Gbps | Always provides a full 40 Gbps bandwidth | |
| Display Connectivity | Supports one display | Supports two 4K displays | |
| USB-C Connector | Utilizes USB-C connector type | Utilizes USB-C connector type | |
| Certification | Devices don’t require certification | Devices are certified for highest standards | |
| Compatibility | All Thunderbolt 4 devices support USB4 | All Thunderbolt 4 devices support USB4 | |
| Cost | Allows for more affordable hubs and docks | Certified Thunderbolt products are premium | |
| Maximum power | Up to 100W | Up to 100W | |
| Identification mark | Iconic USB logo with 20 or 40 | Lightning logo with 4 | |
How fast is lightning communication technology?
Lightning, in the context of data transfer and connectivity, can vary in speed depending on the technology being referred to. If you’re talking about the Thunderbolt 4 or Thunderbolt 3 technology, they both offer a maximum throughput of 40Gbps, which is exceptionally fast for data transfer and peripheral connectivity.
Can Thunderbolt 3 be Used with Thunderbolt 4?
Yes, Thunderbolt 3 can be used with Thunderbolt 4. Thunderbolt™ 4 technology is backward compatible with Thunderbolt™ 3 technology. This means that Thunderbolt 4 ports and devices can work with Thunderbolt 3 cables and peripherals, and vice versa. While you may not be able to take full advantage of the additional features and capabilities of Thunderbolt 4 when using Thunderbolt 3 devices, you can still use them together without any issues.
Can I use Thunderbolt 4 to charge my laptop?
Yes, Thunderbolt 4 can provide power delivery, allowing you to use it to charge your laptop or other devices. It can deliver up to 100 watts of power, making it suitable for charging a wide range of devices, including laptops.
Can I plug USB-C into a Thunderbolt 4 port?
Yes, you can plug a USB-C connector into a Thunderbolt 4 port. Thunderbolt 4 uses the USB Type-C physical connector, which means it’s compatible with USB-C cables and devices. You can use USB-C peripherals with Thunderbolt 4 ports without any issues. However, it’s important to note that while the physical connection is compatible, the capabilities and performance may vary depending on the specific device and cable used.
Which version of Thunderbolt 4 is DisplayPort?
Thunderbolt 4 supports DisplayPort 2.0 to power up to three 10K monitors simultaneously, or one 16K monitor at 60Hz. Thunderbolt 3 supports DP 1.4 and has enough bandwidth to support two 4K (3840 x 2160) displays at 60 Hz, one 4K display at 120 Hz, or a 5K display at 60 Hz.
Is there Thunderbolt 5?
Intel officially launches Thunderbolt 5 in 2023, promising speeds up to 120Gbps, theoretical support for 540Hz gaming monitors, 240W charging power, and more. While the Thunderbolt 5 specification is now official, Thunderbolt 5-enabled accessories and PCs won’t be widely available until 2024. For specific Thunderbolt 5 technical knowledge, please click here to learn more.
Is Thunderbolt 4 better than HDMI?
There are no advantages of HDMI over Thunderbolt in terms of performance. However, the increased performance comes at a higher price and lower compatibility. HDMI’s longer history makes it ubiquitous. If you have a lot of devices with HDMI connectors (input or output) in the early days, they may not support Thunderbolt functionality between them. In-depth knowledge of different versions of HDMI.
How can I use Thunderbolt and HDMI at the same time?
Use an adapter. When using the latest Thunderbolt cables to connect to HDMI devices, you can use an adapter or docking station to convert the connectors and connect them to each other. APPHONE supports this technology. We provide a variety of different connectors and customized production of multi-port adaptation between different versions of technology. to achieve different usage scenarios.
The advancements brought by Thunderbolt 4 make it an indispensable choice for professionals and enthusiasts seeking reliability and unmatched capabilities. With a maximum throughput of 40Gbps, Thunderbolt 4 supports multiple 4K or 8K displays, enables robust data transfer, and delivers substantial power.
As Thunderbolt technology evolves to meet the demands of modern computing, Thunderbolt 4 remains at the forefront, pushing boundaries and unlocking innovative possibilities. The future is bright, with Thunderbolt 4 paving the way for remarkable advancements and seamless connectivity.
At our factory, we specialize in customized mass production of Thunderbolt cables, hubs, and docking stations. We understand the importance of Thunderbolt 4’s cutting-edge performance, and we are committed to providing high-quality solutions tailored to your needs. Contact us today to harness the full potential of Thunderbolt 4 and elevate your connectivity experience.
Share This Artcle:

Fast delivery
Fastest delivery within 22 days

Quick proofing
Fastest 3-day proofing cycle

After-sale protection
24-month long warranty

1V1Customer Service
Professional customer service follow-up








